NPK granulator is a crucial machine used in the production of fertilizer. NPK stands for nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), which are essential elements for plant growth. The granulator is designed to combine these three nutrients in the form of granules, making it easier to handle, transport, and apply to crops. In this passage, we will explore the step-by-step process of using an NPK granulator to make fertilizer, along with some helpful tips and considerations.
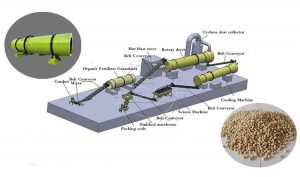
Use drum granulator to make fertilizer
Step 1: Preparing the Raw Materials
The first step in using an NPK granulator is to prepare the raw materials. These materials typically include nitrogen sources such as urea or ammonium nitrate, phosphorus sources like single superphosphate or triple superphosphate, and potassium sources such as potassium chloride or potassium sulfate. It’s important to ensure that the raw materials are of high quality and meet the desired nutrient composition.
Step 2: Mixing the Raw Materials
Once the raw materials are prepared, they need to be thoroughly mixed to achieve a homogeneous blend. This can be done using a fertilizer mixer or a specialized blending machine. The purpose of mixing is to ensure that the nutrients are evenly distributed throughout the mixture, resulting in consistent granule formation.
Step 3: Moisture Adjustment
After the raw materials are mixed, the moisture content of the mixture needs to be adjusted. The ideal moisture level for granulation typically ranges between 2% and 5%. If the moisture content is too low, the granules may not form properly, whereas excessive moisture can lead to caking or sticking issues. Moisture adjustment can be done by adding water or a liquid binder to the mixture and thoroughly mixing it.
Step 4: Granulation Process
The granulation process is the heart of using an NPK granulator. The mixed and moistened material is fed into the granulator, which consists of a rotating drum or disc. Inside the granulator, the material is subjected to a combination of rolling, tumbling, and spraying. During this process, the material forms into granules as the liquid binder or water evaporates. The size and shape of the granules can be controlled by adjusting the speed of the drum or disc and the spraying intensity.

dic pelletizer for sale
Step 5: Drying the Granules
Once the granules are formed, they need to be dried to remove any remaining moisture. This is typically done using a rotary dryer or a fluidized bed dryer. The drying process helps to stabilize the granules, prevent caking, and enhance their storage and handling properties. It’s important to ensure that the granules are dried to the desired moisture content before further processing or packaging.
Step 6: Cooling and Screening
After drying, the granules are usually hot and need to be cooled down before further handling. This can be achieved using a cooling machine or a rotary cooler. Cooling helps to prevent moisture absorption and ensures that the granules maintain their structural integrity. Once cooled, the granules are then screened to remove any oversized or undersized particles, resulting in a uniform size distribution.
Step 7: Optional Coating and Packaging
In some cases, the granules may undergo an additional coating process to improve their appearance, enhance nutrient release, or provide additional functionalities. Coating can be done using various techniques such as spraying a liquid coating agent onto the granules or using a specialized coating machine. After coating, the final step is packaging the granules into bags or containers, ready for distribution and application.
Conclusion and Considerations
Using an NPK granulator to make fertilizer involves a series of well-defined steps, from preparing the raw materials to packaging the final granules. Each step requires careful attention to detail, including the selection of high-quality raw materials, proper mixing and moisture adjustment, controlled granulation, effective drying, cooling, and screening processes. Additionally, it’s essential to consider the specific nutrient requirements of the target crops, as well as regulatory guidelines and environmental considerations.
By following these steps and considering the important factors, one can effectively use an NPK granulator to produce high-quality fertilizers that contribute to the growth and productivity of plants, helping to meet the ever-increasing demands of agricultural practices worldwide.
